Moving to a Synology DS1010+
I’ve been having some trouble with my Windows Home Server involving some potentially misbehaving hardware when put under load. This really only manifests itself when I run PerfectDisk to defrag it, but I’m gathering it’s really a hardware or driver issue and not PerfectDisk’s fault. When you defrag the server will entirely hang up until you reboot it. Occasionally I’ll get file conflicts or lose my backup database. Not great.
Anyway, I have a lot of data stored on that Windows Home Server - terabytes of DVD rips (from discs I own) - and with the problems I’m having, it doesn’t give me a lot of confidence, especially since I can’t turn on file duplication given the size of the data. I don’t have enough storage to handle keeping double copies of it. Not only that, but I’ve noticed that, on occasion, just streaming the DVD rips (not HD, just regular old DVD rips) can get a little slow. Again, not great.
Since the WHS works for music and backups and other videos reasonably well, I figured I’d find a solution to move the DVD rips to and get them off the WHS. Once they’re off, I can remove some of [what I believe to be] the problem drives and figure out what the real issue is. Either way, finding a different NAS solution for my DVDs is a must so if a hard drive goes out, I don’t have to re-rip a bunch of stuff.
I did some research on NAS solutions that support RAID of various levels and I ended up on the Synology DS1010+. Why?
- Speed. Looking at various reviews for NAS devices, Synology devices seem to always be rated high for speed, and usually higher than others.
- Expandability. Most consumer-grade NAS solutions come with a max of four drive bays. After that, you can expand with eSATA (like I did for my Windows Home Server) and be at the mercy of the compatibility of the NAS with the port replicator or whatever. The DS1010+ actually has a specific port replicator that Synology sells that ensures the fast performance you expect and gives you a total of 10 drives’ worth of storage.
- Data protection. As mentioned earlier, I can’t duplicate my DVD rips because I don’t have the room to store everything twice. In a RAID 5 array, though, I have protection for my data if a drive dies but I don’t have to have double the storage capacity to do it.
- Flexibility. This thing appears to be a reasonable answer to WHS as far as features are concerned. You can have it run FTP, iTunes library sharing, DLNA media serving, client PC backup, security camera monitoring/recording, or a ton of other stuff. (I’m not going to do that all immediately; right now, just storing the DVD images is enough.)
- Confidence. This is more a psychological thing, but… after having so many troubles with this WHS and the disks in it, I’ve lost some of the confidence I once had with it. I’ve started compulsively checking the light on the front to see if there’s a “Network Health Critical” warning. I never know if the thing’s going to hang up or fail. I need to find something new I can have some confidence in and put my mind at ease. That’s not a new WHS.
I picked the diskless NAS up at Amazon for $980. Next, drives.
Synology has a compatibility list for the drives it supports in its various devices. For the DS1010+, drives basically fall into two categories: “We’ve tested it and it works” and “It should probably work.” Given my current hardware issues, I wanted drives that were in the “We’ve tested it and it works” category. I wanted 2TB drives, I wanted reasonable performance (it doesn’t have to be an SSD to store DVD rips), and I didn’t want to go broke on it.
I settled on Seagate Barracuda ST32000542AS 2TB 5900RPM drives for $120 each at Amazon. Why?
- Reasonable reviews. I found that unless you get into really expensive drives, most hard drives have poor reviews. The general reason it appears is that sometimes folks will get a DOA drive and instantly go for the one-star rating rather than resolving the issue and then rating the drive proper. You’ll also get the folks who had to call support and had a bad time, which factors in some, but doesn’t really say anything about the drive. Excluding those, it looks like [assuming you get fully functional drives] they’re pretty good.
- Reasonable speed. They’re not 7200 RPM drives, but they are faster than 5400 RPM drives and even appear to compare favorably with some older 7200 RPM drives.
- Price. There’s a gap in 2TB drive pricing between some of the 5400 RPM drives and the faster 7200 RPM drives. Like, it jumps from around $150 drive up to $280 drive without anything in the middle. Price for supposed performance, I couldn’t really beat $120 each.
I picked up four of those drives, so my total cost was $980 + (4 * $120) = $1460. That’s not a cheap bit of kit up front, but if I consider the storage and what I’ve already put in, it’s not that bad.
Interesting side note on my Windows Home Server issue: While I was researching drives, I came across a note in the Synology forums talking about issues people have seen with WD Green drives - the drives I have! Even on the Synology compatibility list you’ll see that there are only a couple of sub-models that performed reasonably in testing. I went through my drives on my WHS and it turns out only about half of them are the decent/peformant models; the others are models that have tested as poor and degrading performance over time. That very well could explain my problems. After I get my DS1010+ set up with all the DVDs moved over, I’ll be removing the problem disks to see if that fixes things.
UPDATE 6/16/2010: Removing the problem drives appears to have stabilized my WHS.
I got the NAS and the disks today. Love that Amazon Prime. Here are the boxes and then the unbox:
I installed all of the drives following the instructions in the quick start guide (very easy), plugged it into my UPS, connected it to the network, and turned it on. Here’s the NAS under my desk. From left to right: Synology DS1010+, Tripp-Lite UPS, Rosewill RSV-S5 eSATA port replicator, and HP EX475 Windows Home Server. You’ll notice that the DS1010+ is about the same size as the Home Server, just laid out horizontally instead of vertically.
Once it was plugged in, it was time to install the firmware. To do that, you use a program called “Synology Assistant” that installs on your client computer. The Assistant detects your NAS and allows you to install the “DSM” or “DiskStation Manager” software/firmware over the network. It’s a lot like installing Windows Home Server in that respect
- the NAS is headless and you install and configure it all over the net.
I downloaded the latest Synology Assistant and DSM patch from the Synology download site rather than using the ones that came on the included CD. I wanted to be sure I had the latest version of everything rather than installing an old version and upgrading later. I unzipped it all in a folder and away I went.
I installed the Synology Assistant and there was a second of panic when I couldn’t find the icon for it in my Start menu - the reason is that I was running as a non-admin user and the installer only installs a shortcut for the user it installs under. In this case, the local machine Administrator was the credential set I entered when the installer asked for better credentials so that’s who got the icon. Rather than log out and log back in, I just ran the DSAssistant.exe program found in the install folder.
After unblocking it from Windows Firewall, I got this screen showing the detection of the DS1010+ and that no firmware was installed.
I double clicked on the server and it took me to an installation screen. First, I selected the DSM “patch” I had downloaded.
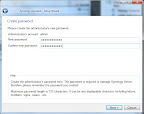
Then I walked through setting up the name of the NAS, the admin password, network settings, etc. Note that I used the “Step By Step” setup rather than the “One-Click.” Seeing as how I left everything as defaults except the administrator password, the one-click setup probably would have been fine.
After finishing the install, I went back to the Synology Assistant management screen (using the icons at the top) and it sort of freaked me out because the server status appeared hung on “Starting services.” I did a manual refresh (using the not-so-intuitive “Search” button) and the status updated to “Ready.”
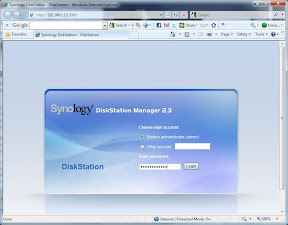
I selected the DiskStation and clicked the “Connect” button which brought up the web interface to log in. I could also have just gone to port 5000 on the DiskStation by manually entering a URL in a browser.
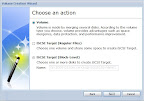
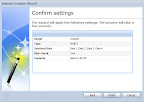
After logging in, I went into the “Management” section and then into Storage -> Volume Manager, which automatically started the Volume Creation Wizard. I used the web-based wizard to create a RAID 5 volume out of the installed disks. Two notes on this:
- I used the “Custom Volume” option rather than the “Standard Volume” option because I wasn’t clear on what would happen in a multi-disk volume in “Standard” mode. I wanted RAID 5, so I specified.
- I selected the option to check/remap all the bad sectors. There shouldn’t be any on the new drives, but I also wanted to do some burn-in/health checking and this appeared to be the way to do it. That said, it takes FOREVER. Click the “go” button and leave it overnight. Note that you don’t have to stay connected to the web-based manager - you can close it up and let it run. To give you an idea, I let it run for about a half hour and got to 7% before deciding to let it be.
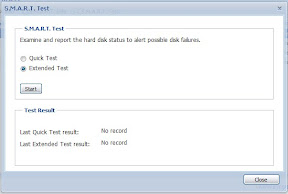
Once the volume was created, I wanted to make sure the disks were running in good order, so I ran an extended SMART Test on them. Granted, it’s not like a major stress test or anything, but it’s good to check what the drive’s reported condition is.
I let that run because the extended test takes 255 minutes. In the end, the results came back “Normal.”
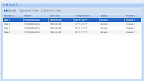
And here’s the detailed info for one of the drives:
So, the disks seem to be working.
I noticed is that these particular drives are not always quiet. When they “woke up” the next morning (I left volume creation running overnight and logged in the next day), there was a noticeable amount of disk noise coming from them. I’d read a little about this in some of the user reviews. During the SMART Test, and even during the volume creation, they were reasonably quiet, but I/O can sometimes be a little noisy. They appear to test out, though, so if it’s just noise, I can handle that. It’s under my desk in the office, not sitting next to my TV while I’m watching a movie.
With the disks tested and ready for content, I had to make sure Windows file sharing was enabled. I also ensured the NAS was in the “WORKGROUP” workgroup so we can use our Windows credentials. (All of my machines are in the default “WORKGROUP” workgroup so this was fine.) Easy enough through the web console:
I then went in and created a user account on the system for all the users in the workgroup. I made sure to give them the same usernames and passwords as on the local machines so the Windows pass-through auth will work.
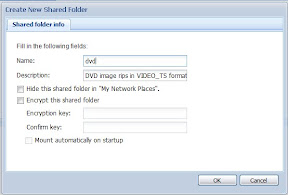
Finally, I had to create a shared folder for my DVDs to be stored in - also easy:
Note that I left the permissions read/write for the default system group. Since all the users are in that group, it means everyone has read/write permissions, which, for my purposes, is perfect.
From a general user standpoint, the web-based management utility is really nice and clean. If you didn’t know better, you’d think you were using a native application. It’s a little more confusing than the WHS console, but then, it also does a lot more right out of the box.
Last thing to do is a little [really rough] speed test. I decided to copy a DVD rip I had made to both the home server and the new NAS. I used the speed estimation thing that shows up in the Windows copy dialog box, so it’s not, like “a benchmark” so much as a general indicator. Also, my laptop only has a 100 Mbit card on it so even though I’m connected to a gigabit switch, it’s negotiating down. (I tried a wireless N connection where I was getting 135 Mbit but various network interference and such, which is horrible in my house, ended up making it slower than a wired 100 Mbit connection.)
Write speed: Copying to Windows Home Server went between 10.5MB/sec and 10.8MB/sec, usually sticking around 10.7MB/sec. Copying to the Synology DS1010+ went between 10.6MB/sec and 11.1MB/sec, usually sticking at 11.0MB/sec. Not the major performance increase I thought it would be, but it’s a little faster.
Read speed: Copying from the Windows Home Server went between 10.9MB/sec and 11.2MB/sec. Copying from the Synology DS1010+ stuck pretty consistently between 11.1MB/sec and 11.3MB/sec. Again, not the major performance increase I thought it would be, but, again, a little faster.
Considering that I’m actually getting some level of data protection and a slight boost in speed, I can’t really complain. With my WHS setup, if a disk goes, I’m re-ripping. With the NAS, I’ve got a little RAID 5 overhead but I’m protected if a disk goes.
Also, again, it’s 100Mbit connection, so ostensibly with an actual gigabit connection I could get 10x the speed. I’d be curious to see the results with that. Maybe I’ll have to get a different adapter or try a different computer.
This sort of helps me in diagnosing some of the issues I’ve been seeing with Windows Media Center and DVD file sharing. I wonder now if maybe my media center PC is potentially a little underpowered to be driving a 1080p display. Maybe. I digress.
All in all, with the benefits listed earlier, I think this is a good move. I think the peace of mind alone will probably make up for the cost. Maybe that’s just me.
Anyway, I’m going to get my DVDs moved over to this and decommission some of the problem drives on my WHS and see how that goes.
UPDATE 5/6/2011: I had an opportunity to talk about my experience with the DS1010+ on the Hanselminutes podcast with Scott Hanselman.